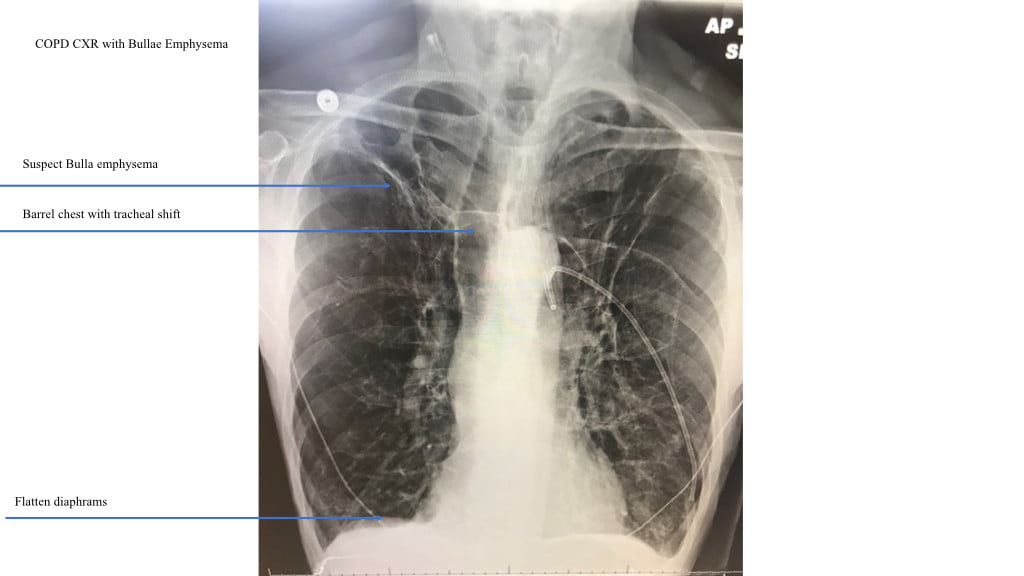
Emphysema: What You Need to Know
Typically, patients with emphysema have good lung compliance but exhibit poor lung elastance.

Typically, patients with emphysema have good lung compliance but exhibit poor lung elastance.
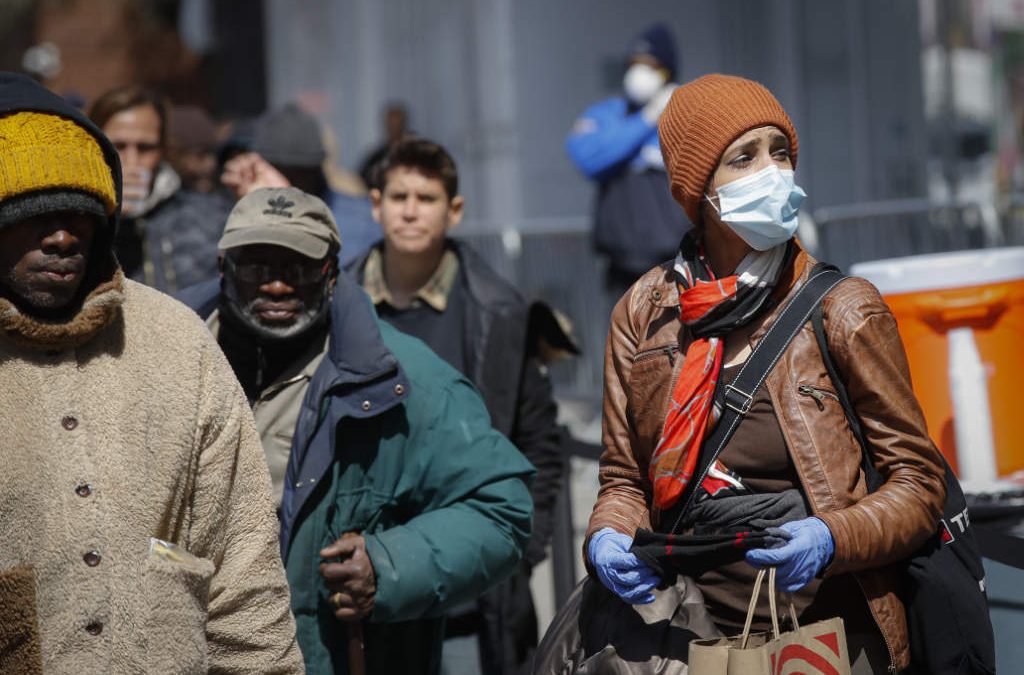

New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo said New York could be six days away from exhausting its supply of ventilators as the statewide death count jumped by more than 400 in 24 hours.
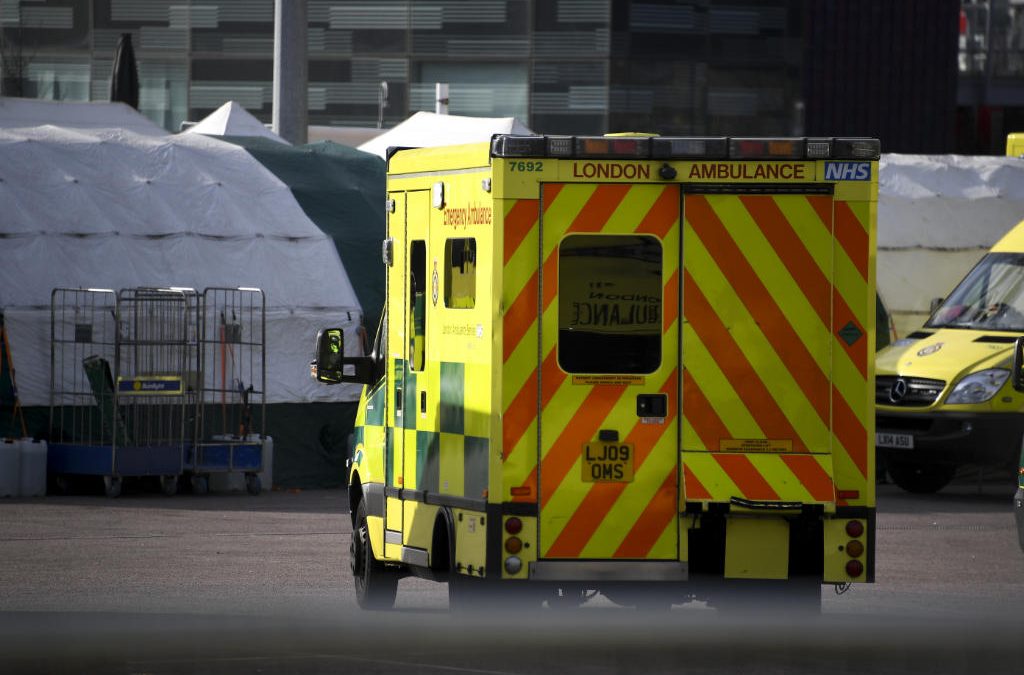

Formula One team Mercedes has helped to develop a breathing aid that could keep coronavirus patients out of intensive care and ease some pressure on Britain’s strained health service.

Given the overwhelming evidence of improved outcomes, prehospital CPAP belongs in every EMS toolbox.
Guidance from the U.S. Centers for Disease and Prevention, current as of March 10, 2020.

This paper provides an overview of pulmonary hypertension in the prehospital setting, including pathophysiology and identification.
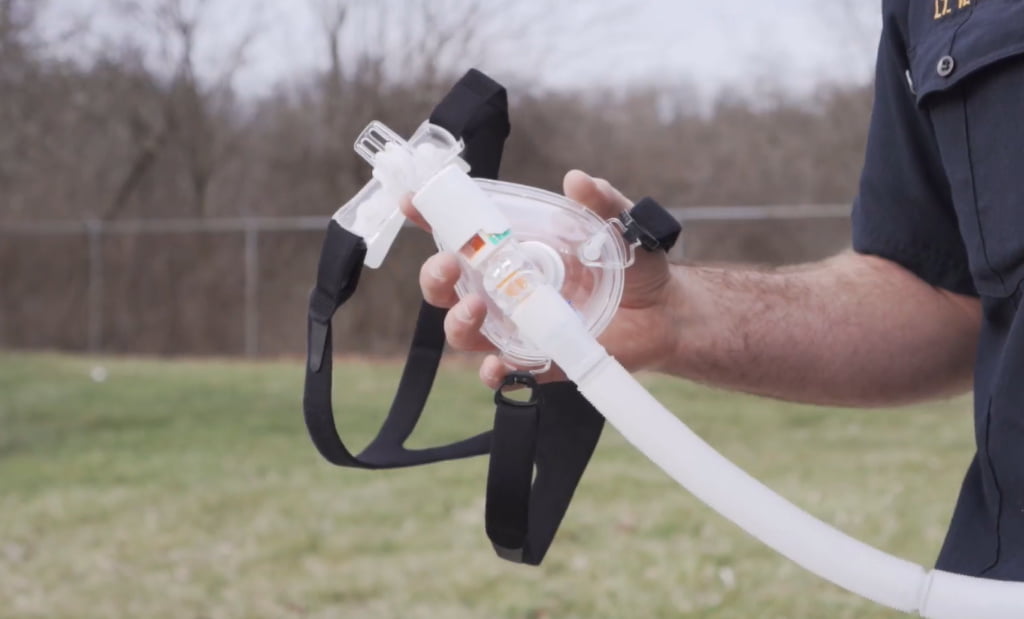

Medics in Westerville, Ohio have partner with Nationwide Children’s Hospital to receive pediatric CPAP equipment.
Pulmodyne, Inc. is now the U.S. Exclusive Master Distributor of the Naso-Flo®, and the new Naso-Flo2® product line.
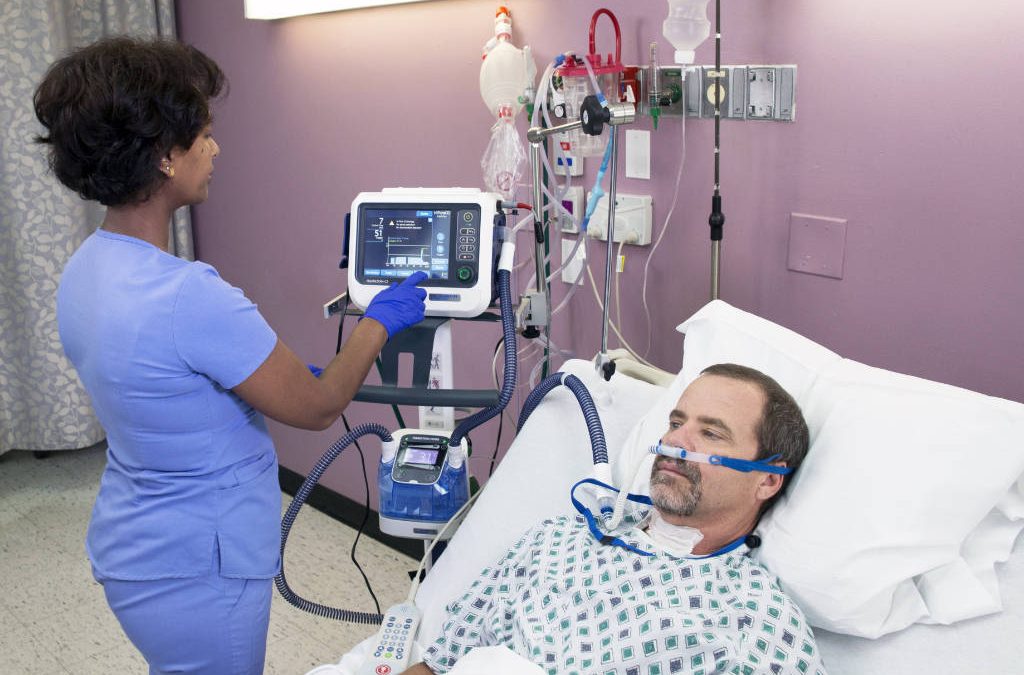
Why the early application of high-flow nasal cannula in the appropriate patient population is an ideal way to meet the patient’s inspiratory flow demand.
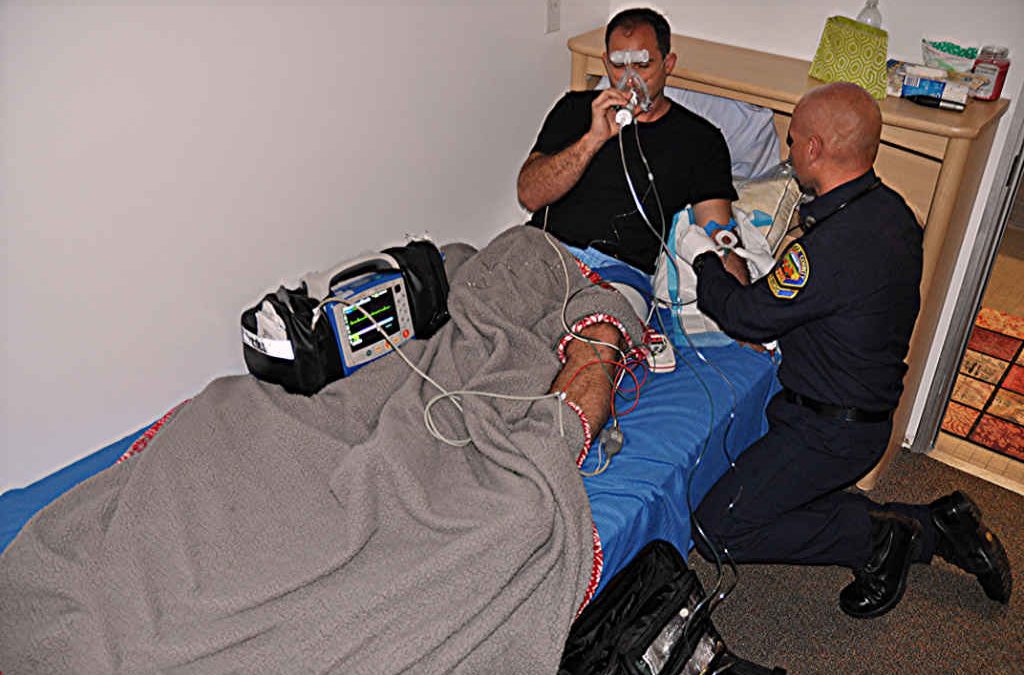
Acute respiratory distress is a serious emergency. Good patient outcomes require a skilled assessment of the airway, breathing and oxygenation.
Recent Comments